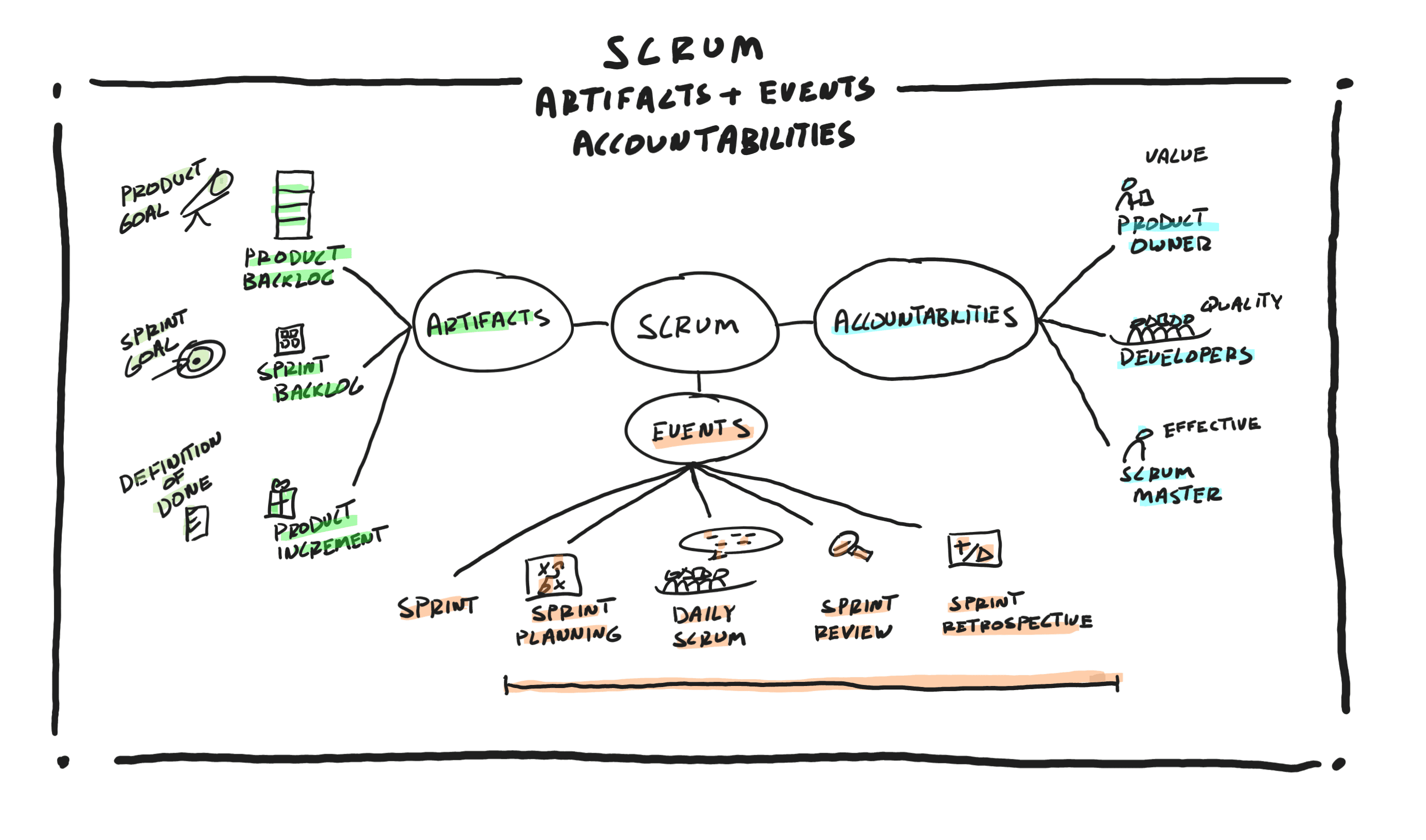
In Scrum, there are 3 accountabilities, 3 artifacts, and 5 events.
The 3 accountabilities in Scrum are:
- Product Owner, accountable for the delivery of a valuable product.
- Developers, accountable for building and delivering a working quality product.
- Scrum Master, accountable for the effectiveness of the Scrum team and organization in building and delivering a valuable, quality, working product.
The 3 artifacts in Scrum are:
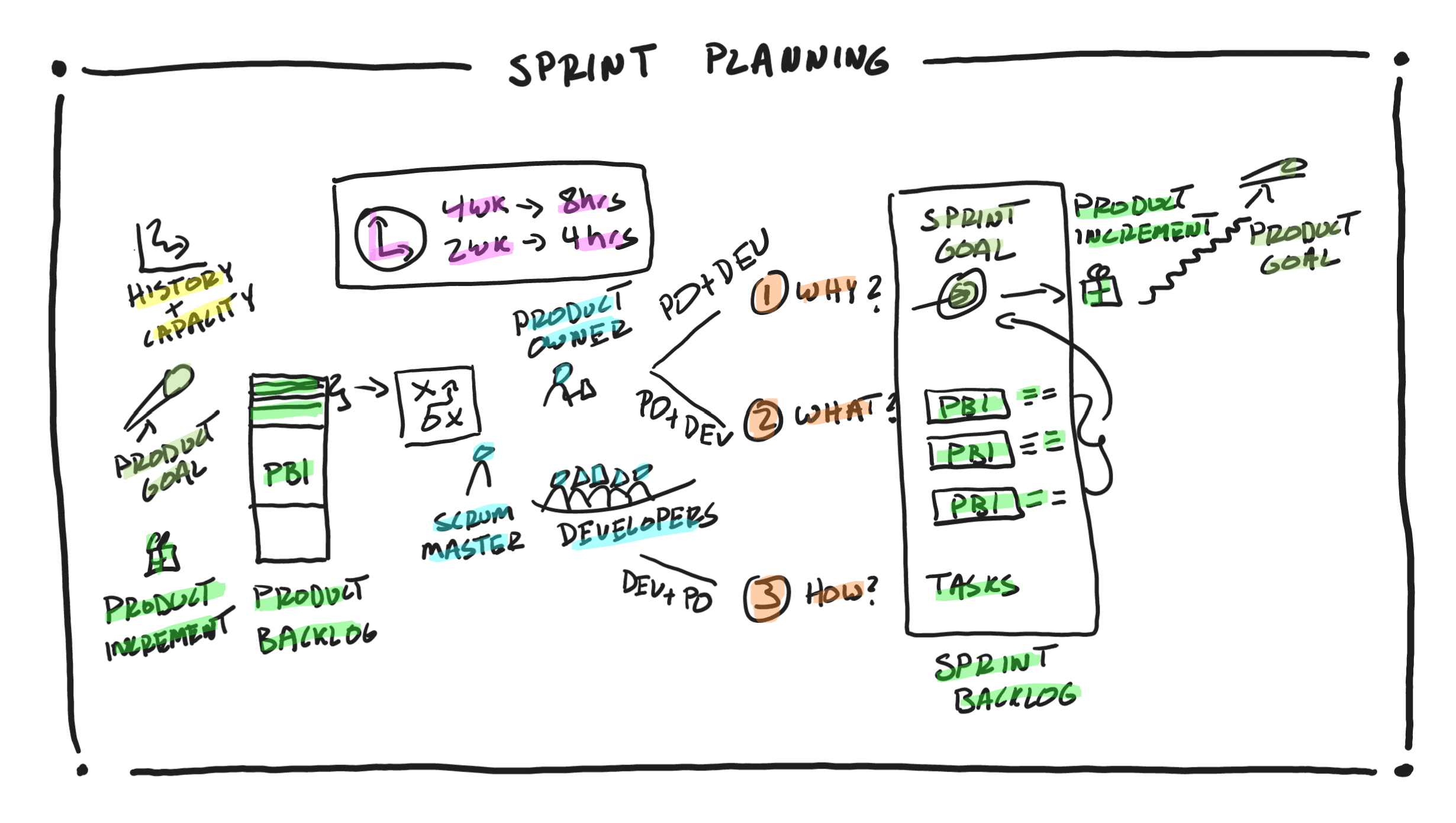
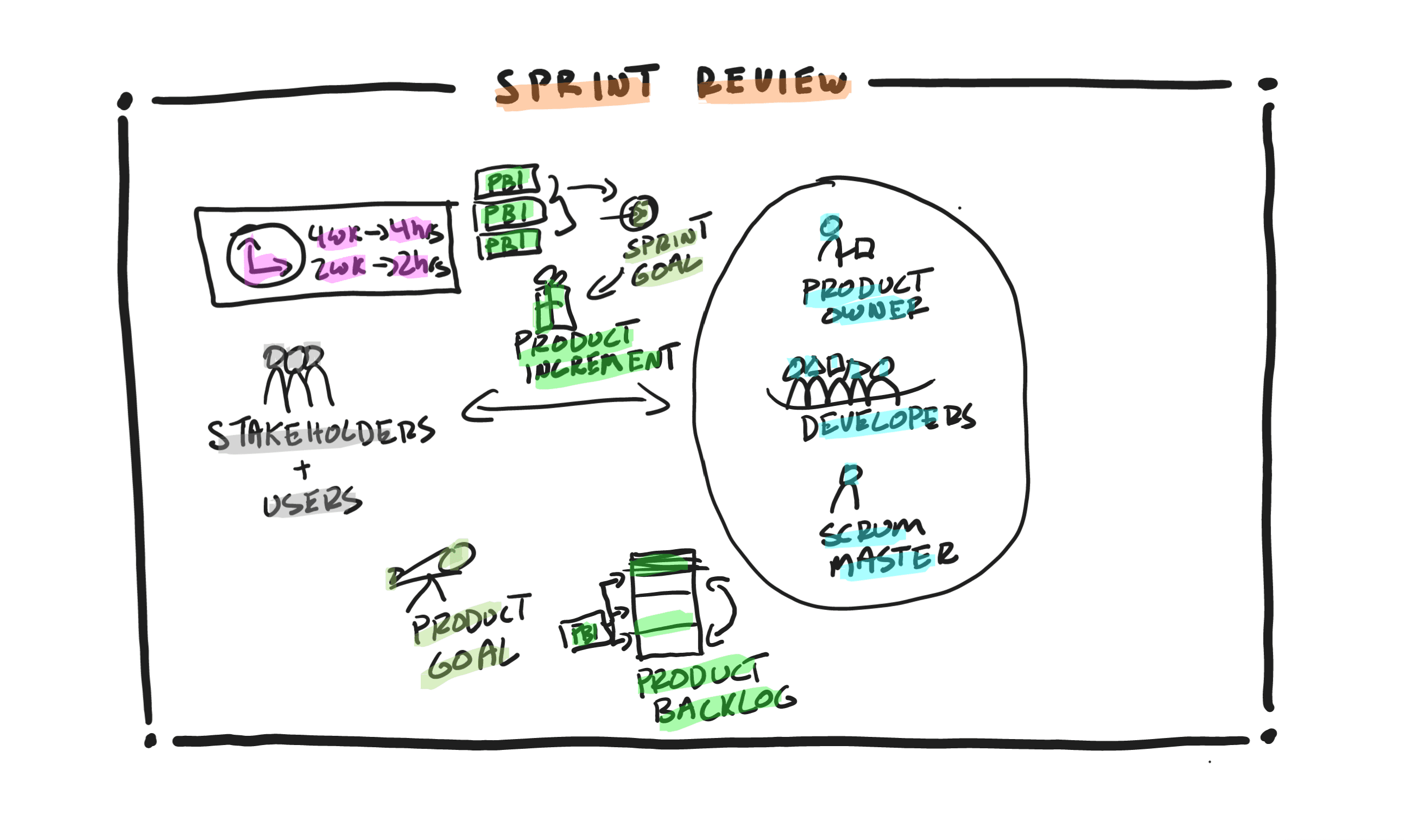
- Product Backlog, an order list of Product Backlog Items that emerges from the Product Goal and includes hypotheses, requirements, features, enhancements, etc.
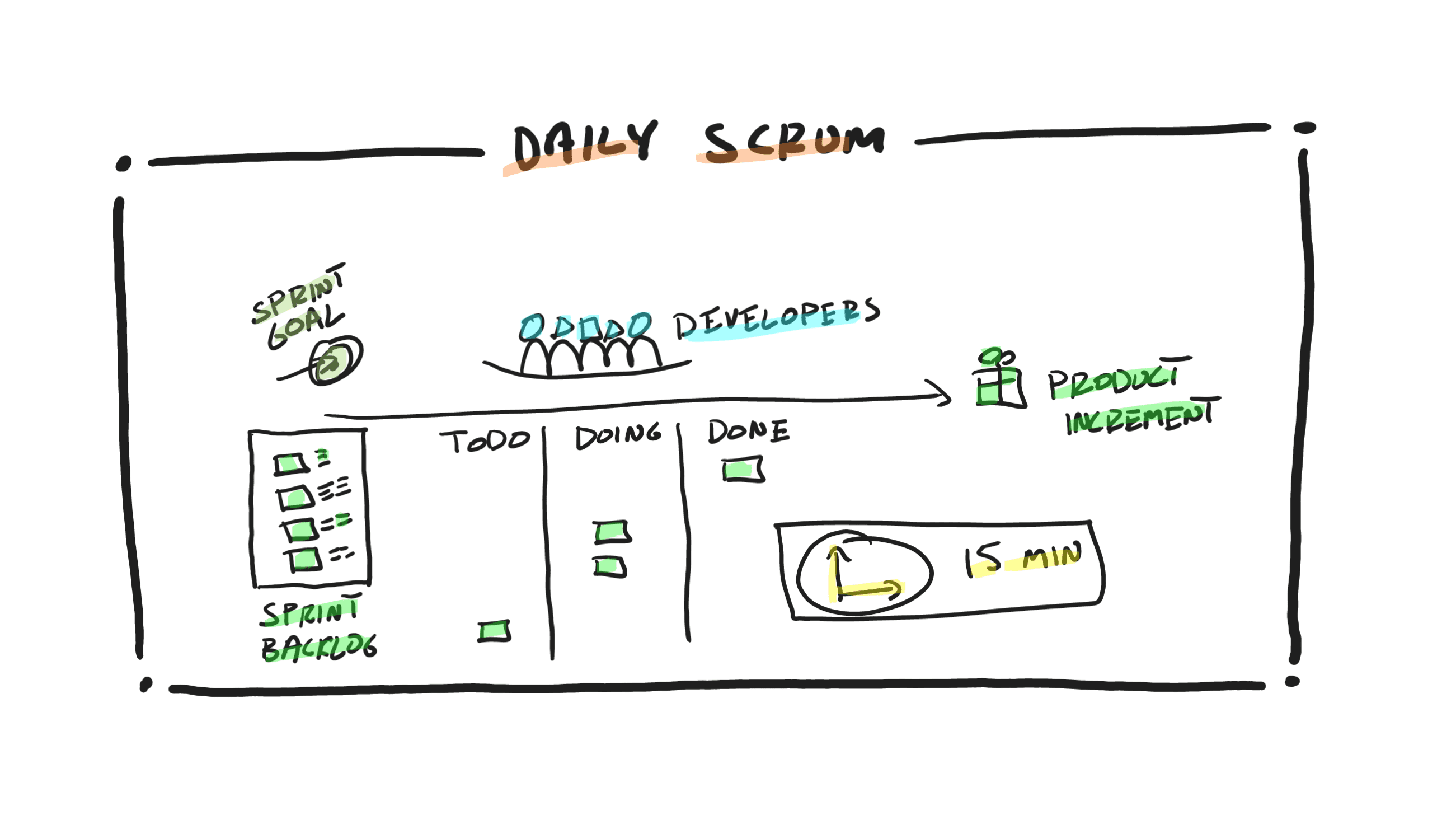
- Sprint Backlog, the team’s plan to accomplish the work for the Sprint. It includes a Sprint Goal, a cohesive set of Product Backlog Items pulled from the Product Backlog that help accomplish the Sprint Goal, and a list of tasks needed to complete the Product Backlog Items and accomplish the Sprint Goal.
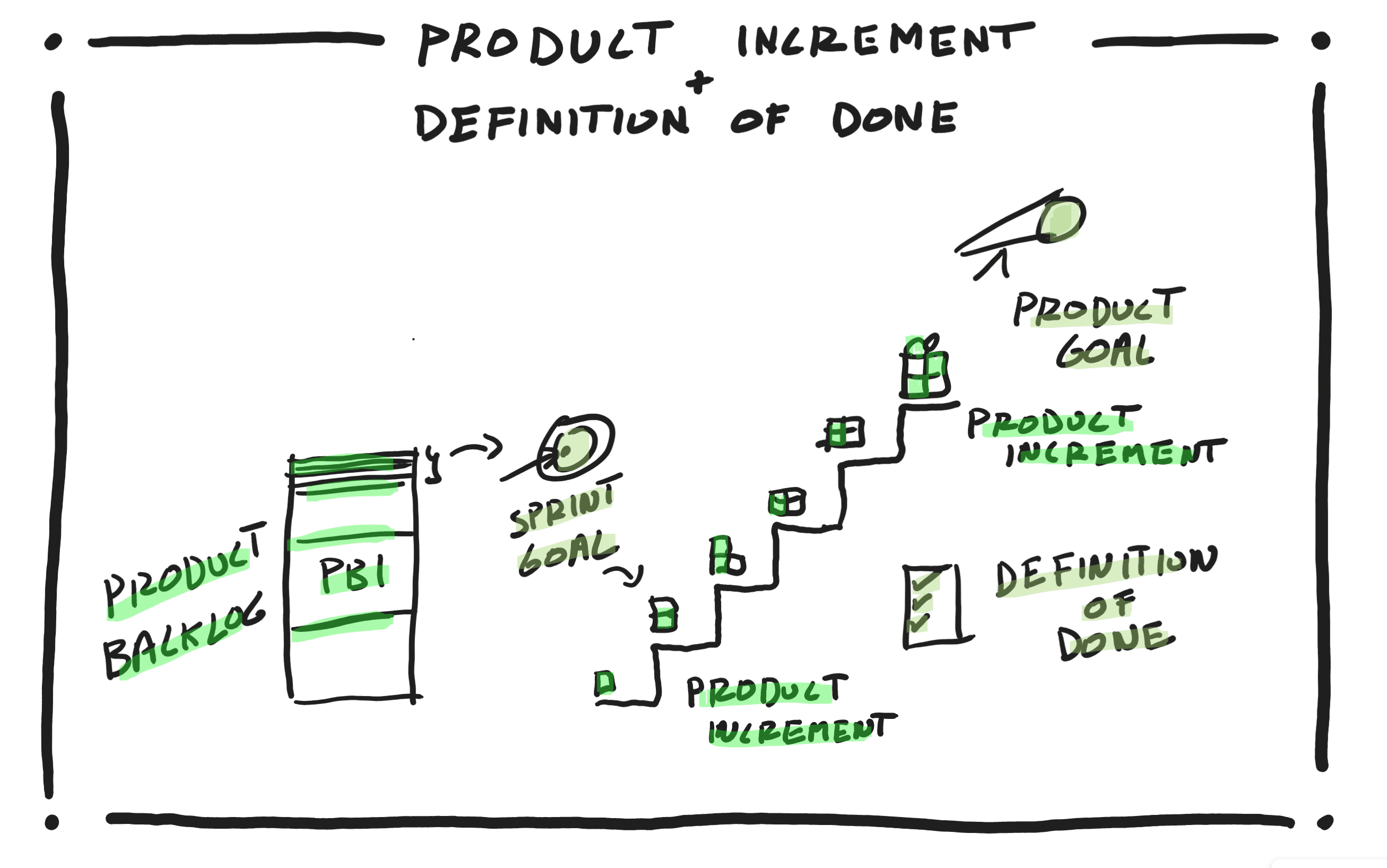
- Product Increment, the output of every Sprint. It is a useful, valuable, usable, and working increment that is at a level of quality as per the team’s Definition of Done. It includes all the previously built increments in addition to what was just built in this Sprint.
- The Product Goal, Sprint Goal, and Definition of Done are referred to as commitments in Scrum. The Scrum team commits to delivering a Product Increment that meets the Sprint Goal, is at a level of quality as per the team’s Definition of Done, and gets them one step closer to the Product Goal.
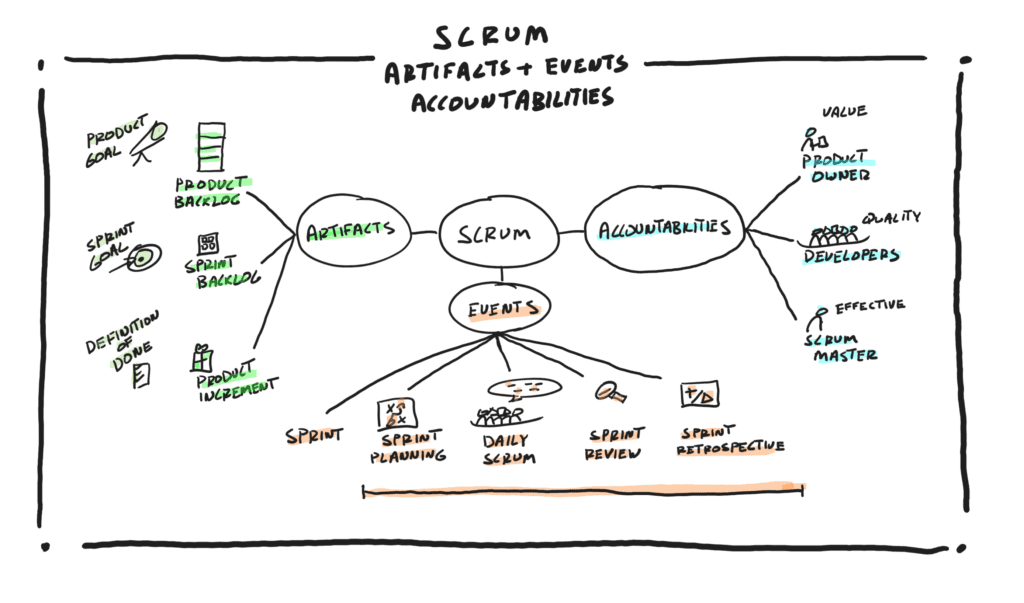
The 5 events in Scrum are:
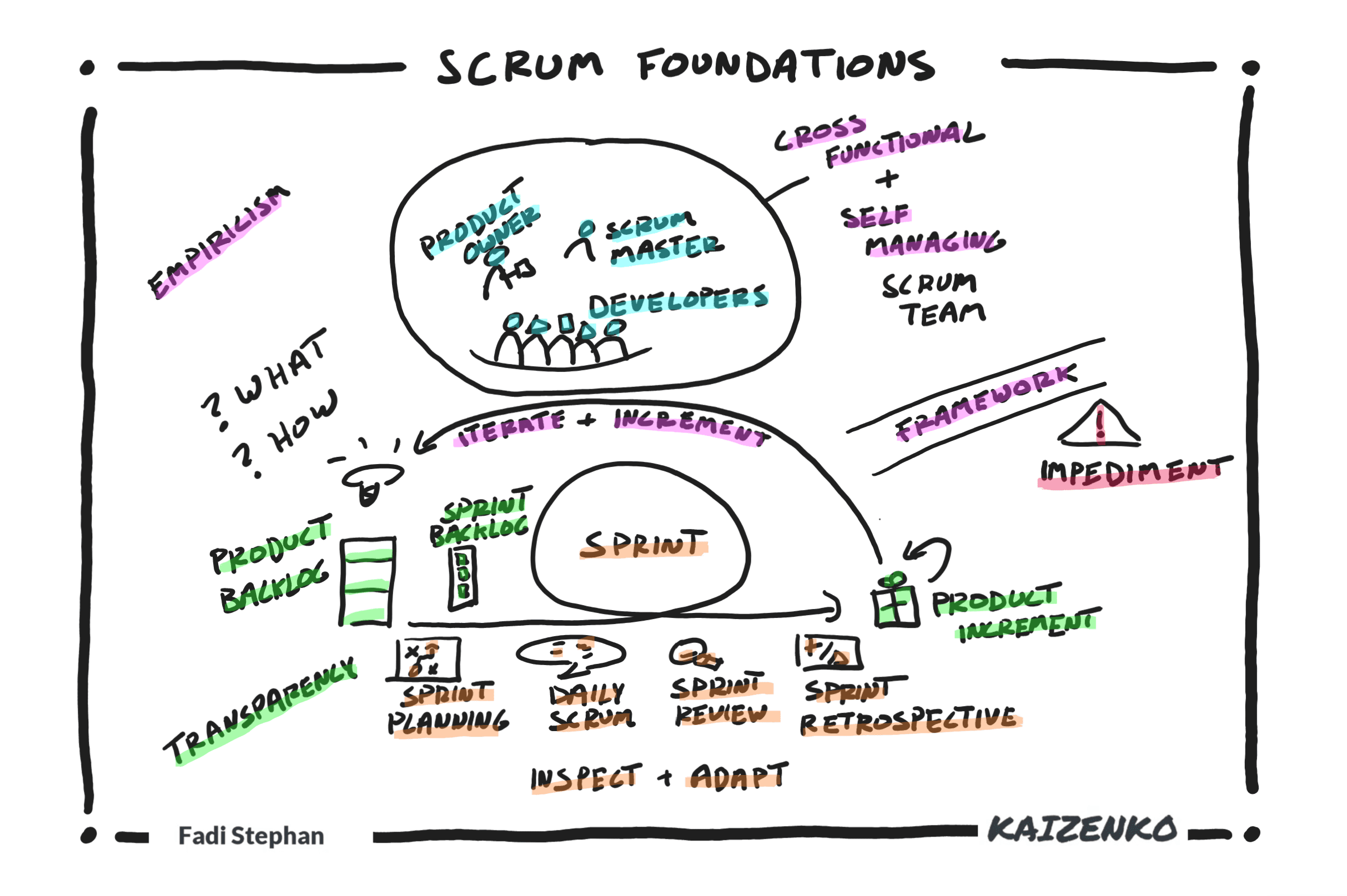
- The Sprint, a fixed duration with a specific start time and a specific end time. A Sprint is less than 30 days. Once a Scrum team decides on the length of the Sprint, every Sprint will be the same length from Sprint to Sprint as the team establishes a regular cadence and work rhythm. Instead of changing the size of the Sprint to fit the upcoming work, the team breaks down the work into more manageable pieces to fit within the Sprint. The Sprint is a container event for all the other Sprint events of Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
- Sprint Planning, a planning event at the beginning of each Sprint to inspect the Product Backlog, the progress made toward the Product Goal based on the latest Product Increment, and adapt or create the Sprint Backlog and the team’s plan to accomplish the work for the current Sprint. This includes establishing a Sprint Goal, pulling a cohesive set of Product Backlog Items from the Product Backlog that will help accomplish the Sprint Goal, and then task out the work needed to complete each pulled Product Backlog Item.
- Daily Scrum, a daily planning event by the Developers to inspect their work and the progress they are making toward the Sprint Goal, and then plan their day accordingly by adapting, adjusting, and updating the Sprint plan known as the Sprint Backlog.
- Sprint Review, a collaborative working session with the stakeholders towards the end of each Sprint to determine the progress made towards the Product Goal by inspecting the Product Increment, getting feedback on it and then adapting and updating the Product Backlog accordingly, thus ensuring the Scrum team is always working on the most valuable items.
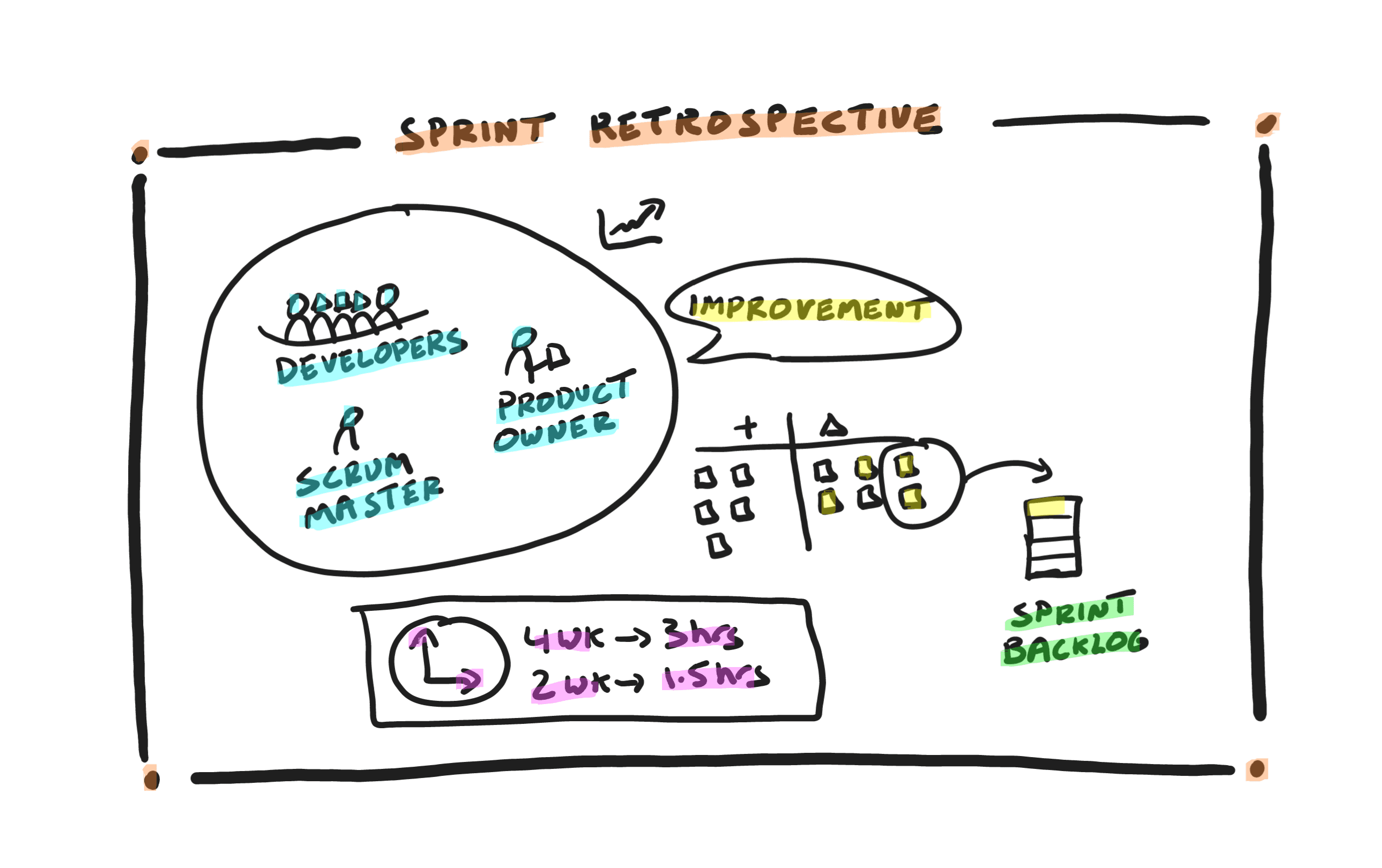
- Sprint Retrospective, a reflection event at the end of each Sprint for the Scrum team to inspect their team dynamics, relationships, tools, and processes and then come up with a continuous improvement plan for the team and organization to adapt and become more effective.
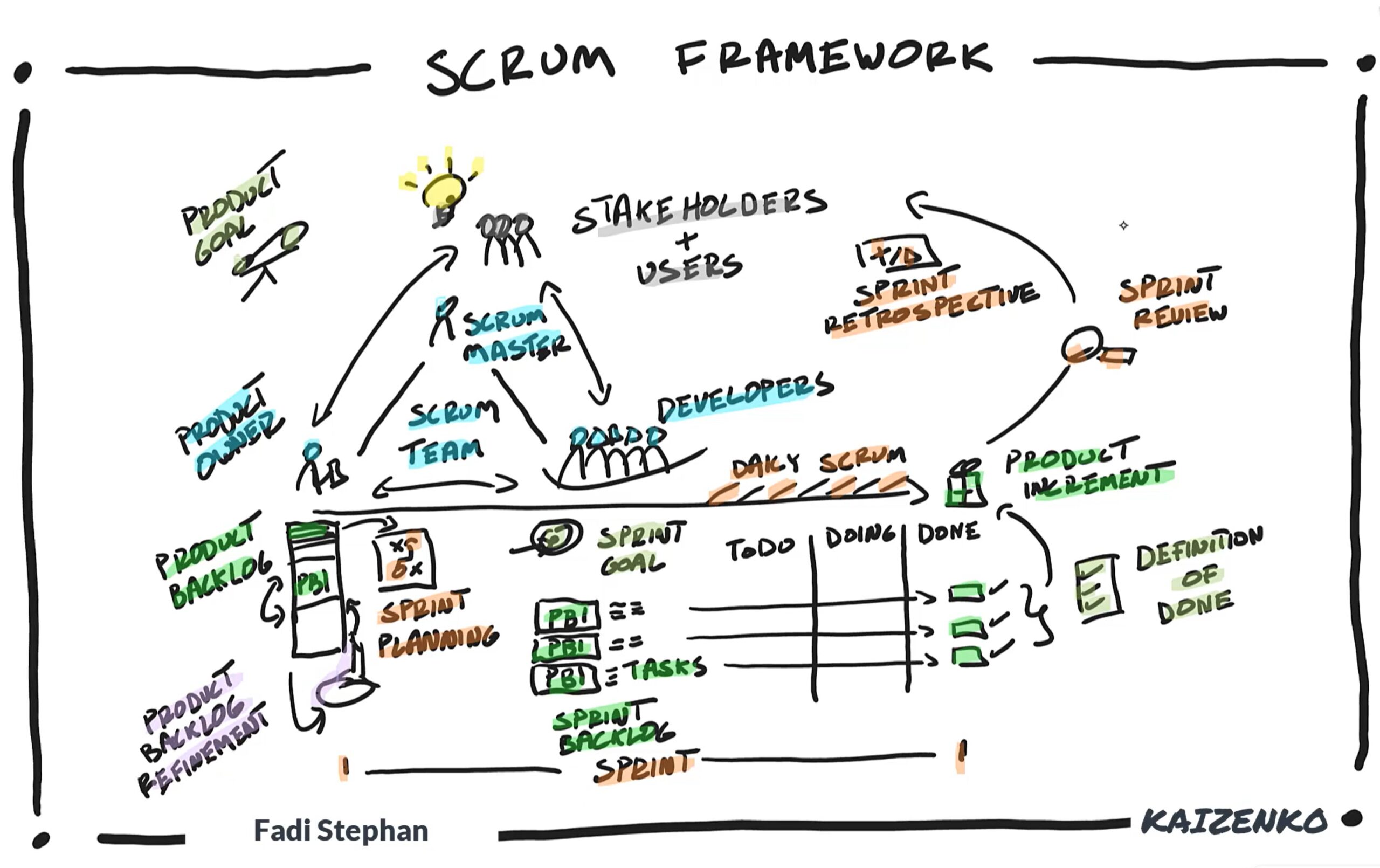
And that’s the Scrum Framework as defined by
- It’s 3 accountabilities of Product Owner, Developers, and Scrum Master.
- It’s 3 artifacts: The Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Product Increment along with the 3 commitments of the Product Goal, Sprint Goal, and Definition of Done.
- It’s 5 events: The Sprint, and within the Sprint, Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
For more details, sign up for an upcoming foundational ScrumMaster® (CSM®) class or a Certified Product Owner® (CSPO®) class or Certified Scrum Developer® (CSD®) class.
Next check out the entire Scrum in a Nutshell series:
Scrum in a Nutshell
Scrum is a framework for developing, delivering, and sustaining complex products. It all starts out with our stakeholders, customers, and users that have an idea about a product they need and want developed. They collaborate directly with Developers to turn this idea into reality. Developers in Scrum are not just programmers. They are part of…
Scrum Accountabilities, Artifacts, and Events in a Nutshell
In Scrum, there are 3 accountabilities, 3 artifacts, and 5 events. The 3 accountabilities in Scrum are: The 3 artifacts in Scrum are: The 5 events in Scrum are: And that’s the Scrum Framework as defined by
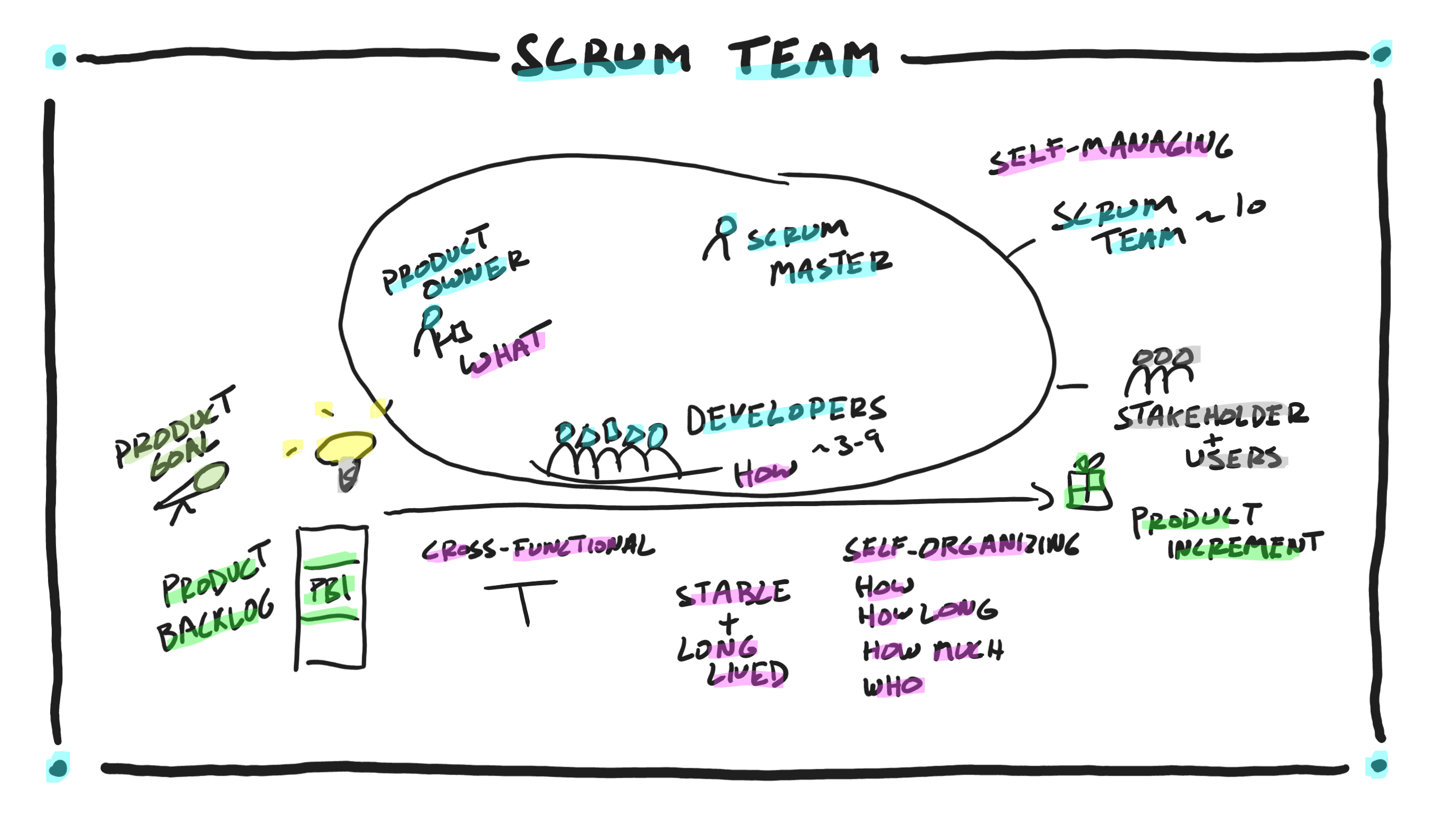
Scrum Team in a Nutshell
The Scrum team consists of 3 accountabilities, Developers, Product Owner, and Scrum Master. Developers are accountable for building and delivering a quality working Product Increment at the end of each Sprint. They are a small group, typically 3 to 9 members that are cross-functional and self-organizing. Developers are cross-functional to remove bottlenecks and dependencies. Developers…
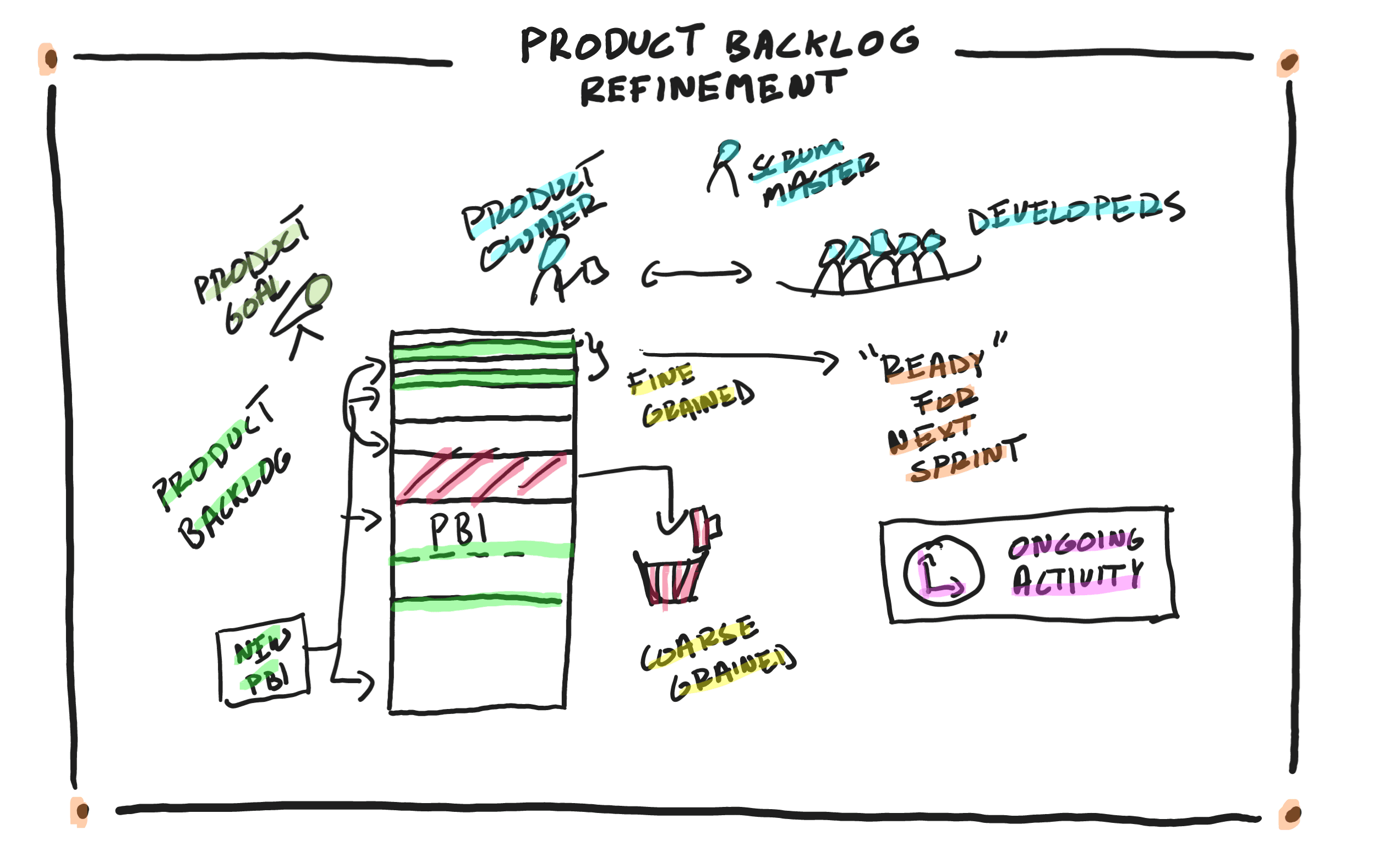
Product Backlog Refinement in a Nutshell
The Product Backlog is an ordered list of hypotheses, requirements, features, enhancements, or Product Backlog Items that help the team accomplish the Product Goal. The Product Backlog is the team’s single source of work. Meaning, anything the Developers are working on should be coming from the Product Backlog. There are no side requests. Any work…
Sprint Planning in a Nutshell
In Scrum, the Sprint starts with Sprint Planning where the Scrum team plans out their work for the Sprint and creates a Sprint Backlog. The Sprint Backlog is the team’s plan to accomplish the work. Sprint planning is timeboxed to 2 hours per week of Sprint, so for a 2-week Sprint it is one event…
Daily Scrum in a Nutshell
The Daily Scrum is a brief daily planning event by the Developers to inspect their work and the progress they are making toward the Sprint Goal that will result in a Product Increment. The Developers created their Sprint plan or Sprint Backlog in Sprint Planning at the beginning of the Sprint. However, this plan is…
Sprint Review in a Nutshell
The Sprint Review is a working session for the stakeholders, users, and customers to collaborate with the Scrum team which includes the Developers, Product Owner, and Scrum Master, and inspect the progress made toward the Product Goal based on the latest Product Increment. The Sprint Review is about getting feedback from the stakeholders and users…
Sprint Retrospective in a Nutshell
The Sprint Retrospective is a reflection event that occurs at the end of each Sprint. It is for the entire Scrum team which includes the Product Owner, Developers, and ScrumMaster to inspect how they are operating and then come up with a continuous improvement plan to adapt and become more effective as a team and…
Product Increment and the Definition of Done in a Nutshell
The Product Increment is the output of every Sprint and is an increment that brings the team one step closer to the overall Product Goal. This means that each Sprint is focused on a cohesive set of Product Backlog Items that meet a Sprint Goal and not random unrelated items. Once a Sprint starts and…
Scrum Values in a Nutshell
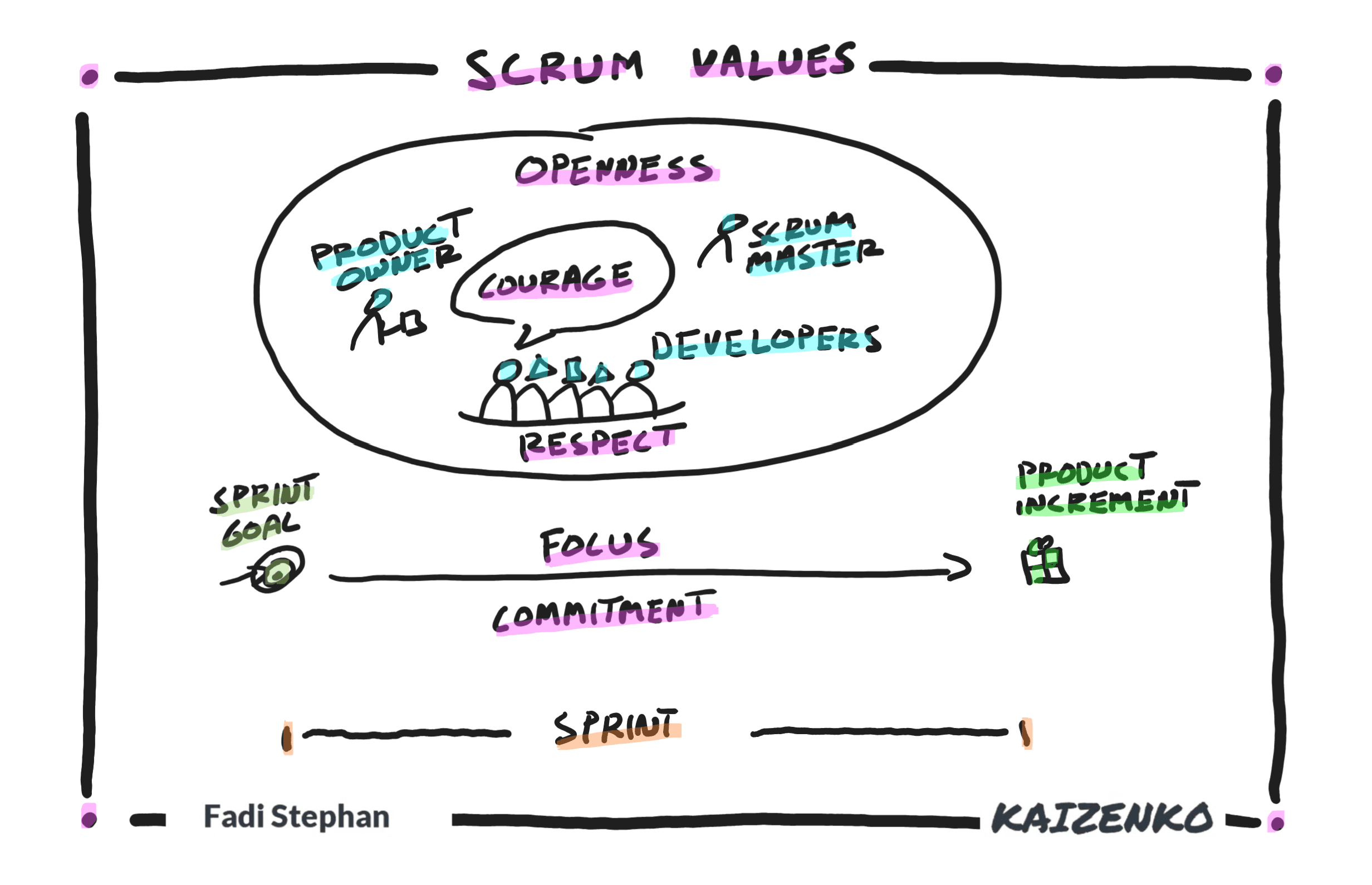
For teams to succeed with Scrum, team members must become proficient in living the 5 Scrum values of commitment, focus, openness, respect, and courage. Commitment: In Scrum, the team commits to each other, not to other people, but to each other, on supporting each other to deliver on the Sprint Goal and Product Goal. Focus:…
Scrum Foundations and Theory in a Nutshell
Scrum is a framework for solving complex adaptive problems with high levels of unknowns, uncertainties, or risks around what to build or how to build it. Scrum involves a cross-functional and self-managing Scrum team that uses empiricism to build products iteratively and incrementally to reduce risk and deliver early and often. The Scrum team uses…
Scrum and the Manifesto for Agile Software Development
Back in February 2001, at the lodge in Snowbird Utah, 17 thought leaders from the software industry got together to discuss the state of software development and compare various lightweight frameworks that popped up in the late 90s because of dissatisfaction with the traditional waterfall approach to building products. The participants shared and learned about…